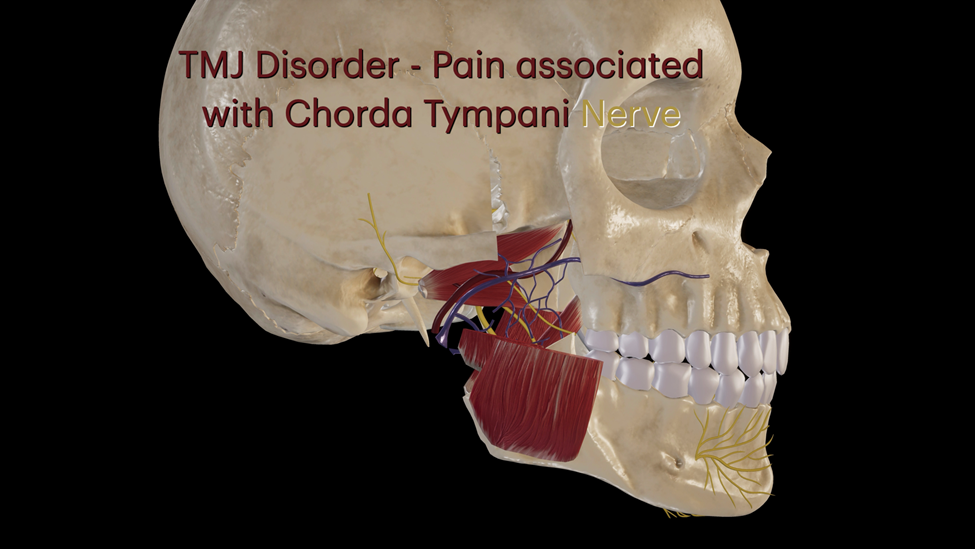
Patients suffering from TMJ Disorder can experience various symptoms including pain, tingling, numbness, vertigo (dizziness) and referred pain to other parts of face, head, neck and arms.
Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD) can lead to pain in the chorda tympani nerve due to its anatomical proximity to the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and associated structures. The chorda tympani, a branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), passes near the TMJ and provides taste sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, as well as contributing to the innervation of the salivary glands. When TMD causes inflammation, swelling, or misalignment of the TMJ, the resulting pressure or injury can impinge on the chorda tympani nerve. This compression or irritation can lead to referred pain, altered taste sensation, or even neuralgia, highlighting the interconnectedness of the craniofacial nerves and the complexity of TMD-related symptoms.
Damage to the chorda tympani nerve can result in several distinct signs and symptoms. The chorda tympani nerve plays a key role in taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and also contributes to the parasympathetic innervation of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Here are the potential signs and symptoms of damage to this nerve:
- Altered Taste Sensation (Dysgeusia or Ageusia):
Loss of taste (ageusia) or altered taste (dysgeusia) in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is one of the most common symptoms. This might manifest as a metallic, salty, or otherwise abnormal taste sensation.
- Decreased Salivation:
A reduction in the production of saliva from the submandibular and sublingual glands may occur, leading to a dry mouth (xerostomia). This could affect oral health, speech, and swallowing.
- Hyperacusis:
Although more associated with facial nerve damage, some patients might experience an increased sensitivity to sound (hyperacusis) if there is concurrent involvement of the facial nerve near its origin, as the chorda tympani passes close to the middle ear.
- Lingual Nerve Involvement:
If the chorda tympani damage occurs near its junction with the lingual nerve, there could be associated symptoms such as numbness or tingling in the tongue.
- Burning Mouth Syndrome:
In some cases, patients might experience a burning sensation in the mouth, particularly in the region where taste is affected.
It’s worth noting that damage to the chorda tympani nerve is often related to surgical procedures involving the ear, such as middle ear surgery, or as a result of trauma or infections in the area. Damage can also occur in Temporo-Mandibular Disorder where the mandible is retruded and the condyle distallized. Understanding the intricate anatomy of the TMJ as well as symptoms of nerve damage helps the clinician in providing a correct diagnosis and treatment for those suffering with TMD.